Single sign-on
Single sign-on for Ntlm and Kerberos is a Xima® Formcycle license module which is subject to additional costs.
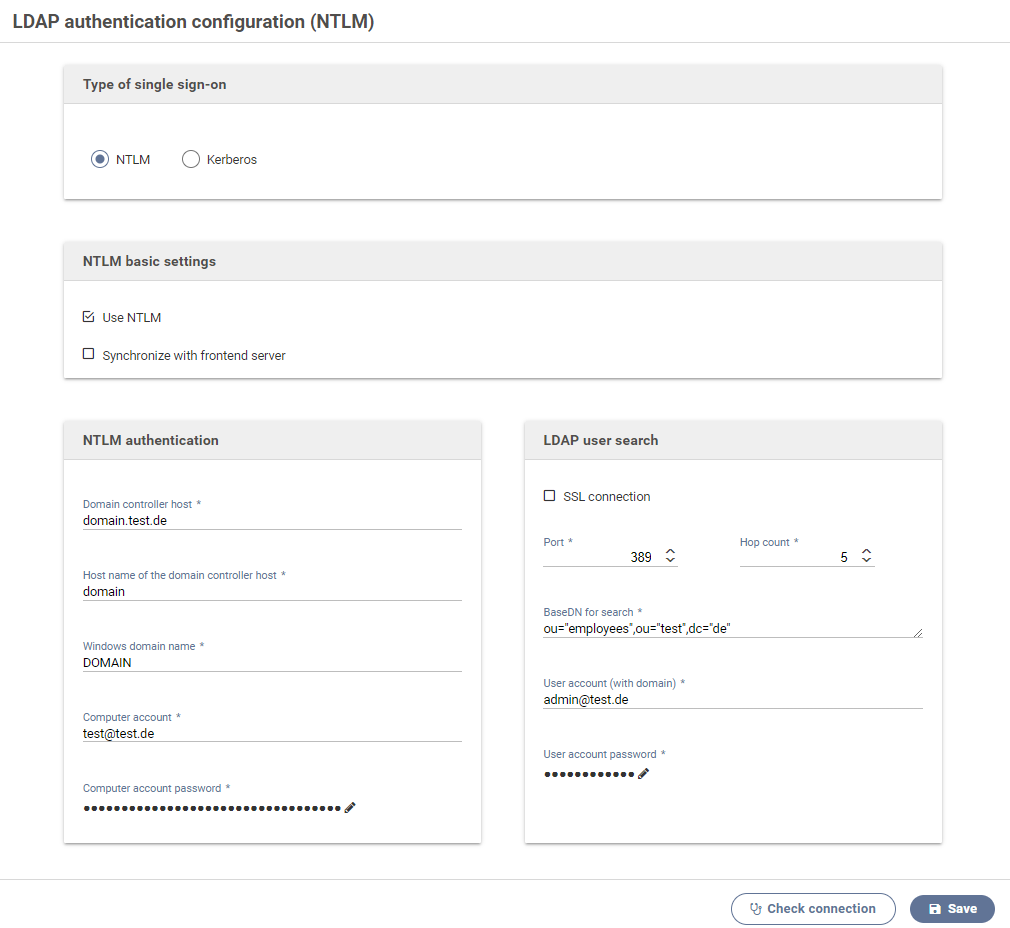
Ntlm (NT LAN Manager) can be used to authenticate users of a form.
A common use case are forms used internally by some company, and that may be accessed only by the employees of that company. The user data of the active directory can be accessed via Ntlm.
Using NTLM
Activate this option to use Ntlm.
Synchronize with frontend server
Activate this option to transmit the current configuration to all connected and available frontend servers when saving these settings.
Domain controller host
The host (FQN) of the active directory controller used for authenticating users via Ntlm and transmitting their data over Ldap.
Connection to the Ldap server for the Ldap search account has been established successfully
NTLM authentication
The following settings are required for enabling users to authenticate via Ntlm.
Host name of the domain controller host
The host name of the active directory controller.
Windows domain name
Different forms of the domain name can be used depending on the active directory.
Computer account
The computer account must have been granted permission to perform user verification. It must not be a regular user account.
We are currently unable to provide a description of the procedure for creating a computer account in the Active Directory server and this must be referred from external sources in the relevant documentation.
computer account password
Password of the computer account.
LDAP user lookup
The following settings concern the user lookup after a successful Ntlm authenication.
Port
The port for connecting to the Ldap server for the user lookup.
SSL encryption
Enables SSL encryption when communicating the the Ldap server.
Hop count
The number of hop counts or referrals. Setting this to 0 disables following references.
User account (with domain)
Account to be used for looking up users. It must have been granted permission to perform user lookup.
User account password
Password of the user account.
Base DN für user lookup
Ldap base DN used for looking up authenticated users.
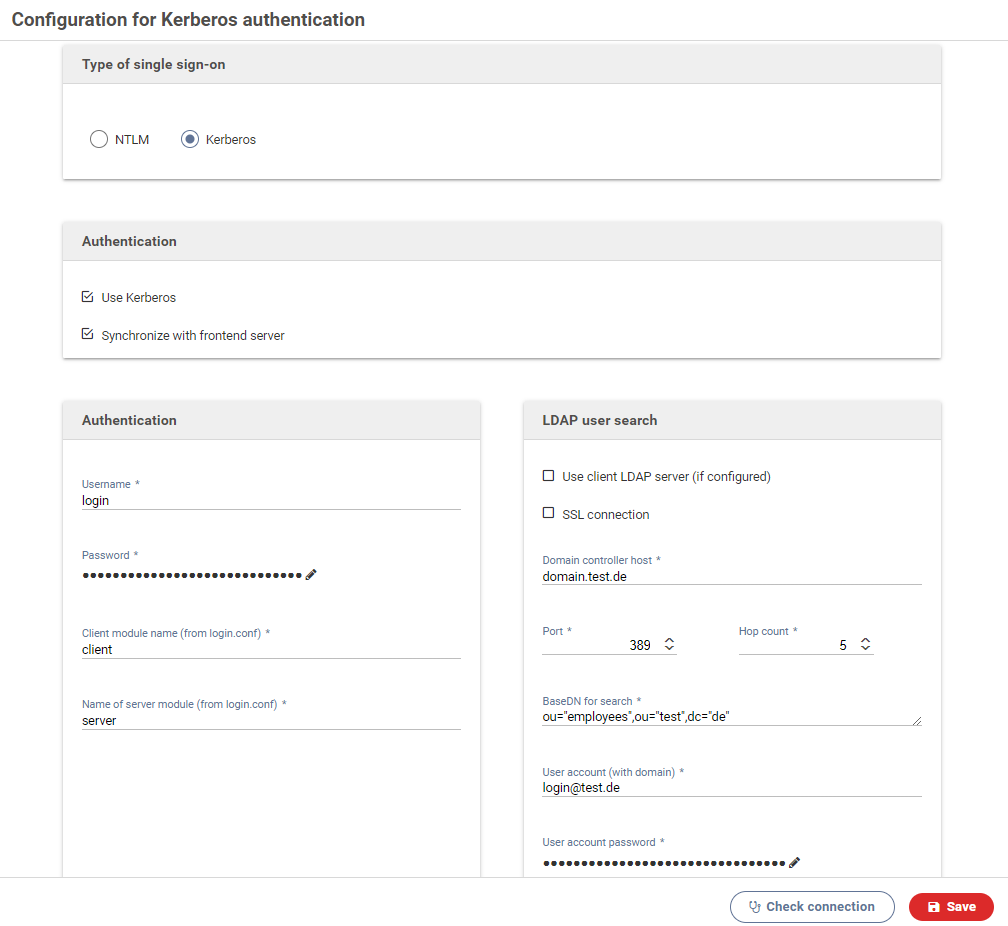
Settings for Kerberos authentication
Kerberos can be used to authenticate form users. This is often used for internal forms meant only for the employees of a company. The data of the current user can be retrieved from an active directory as well.
Kerberos authentication is available only when the license includes this option.
Use Kerberos
Activate this switch to enable Kerberos authentication.
Synchronize with frontend server
When activated, all changes to the configuration will be sent to all available frontend servers.
Username
The Window Domain account required for accessing the Key Distribution Center (KDC) and beginning the authentication process.
Normally this is the user account of the active directory that is setup as a service account.
Password
Password of the service account.
File krb5.conf
Enter the content of the file krb5.conf, ie. the configuration file for Kerberos.
Among other settings, the available encryption methods, the current real and its mapping to a KDC should be set.
File structure
The file format is similar to Windows INI files. It contains of individual sections, introduced by their names in brackets. Each section may or may not contain several key-value pairs:
or
foo = bar
some = input
}
Section names
[libdefaults]
Contains settings used by the Kerberos library v5.[realms]}} Realm-specific settings and contact information.{{/litem}}
- {{litem title=
A list of supported session key encryption methods that should be requested by the client when performing an AS (authentication server) request. The priority of each method is given by the order in which they have been specified, the first one being the method with the highest priority. Several methods can be separated with commas or spaces.
- {{litem title=
- {{litem title="default_tgs_enctypes}}A list of supported session key encryption methods that should be requested by the client when performing a TGS (ticket granting server) request. The priority of each method is given by the order in which they have been specified, the first one being the method with the highest priority. Several methods can be separated with commas or spaces.{{/litem}}
permitted_enctypes
- A list of all allowed session key encryption methods.
A simple configuration for the [libdefaults] section might look as follows:
default_realm = EXAMPLE.COM
default_tkt_enctypes = aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96 aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96 des3-cbc-sha1 arcfour-hmac-md5 camellia256-cts-cmac camellia128-cts-cmac des-cbc-crc des-cbc-md5 des-cbc-md4
default_tgs_enctypes = aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96 aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96 des3-cbc-sha1 arcfour-hmac-md5 camellia256-cts-cmac camellia128-cts-cmac des-cbc-crc des-cbc-md5 des-cbc-md4
permitted_enctypes = aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96 aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96 des3-cbc-sha1 arcfour-hmac-md5 camellia256-cts-cmac camellia128-cts-cmac des-cbc-crc des-cbc-md5 des-cbc-md4
[realms]
Each key in the [realms] section represents the name of a Kerberos realm. The value is a list of mappings, defining the properties of each realm. The following properties can be set:
- kdc: The name or address of a server running a KDC (key distribution center) for this realm, usually the server with the active directory. When necessary, the port number can be specified by appending it separated by a column.
A simple configuration for the [realms] section might look as follows:
EXAMPLE.COM = {
kdc = domain.example.com
}
[domain_realm]
The section [domain_realm] contains a mapping from domain names or host names to Kerberos realm names. The key can be a host or domain name, but domain names must be prefixed with a period. The value must be the name of a Kerberos realm for this host or domain. Host and domain names should be spelled with lower case letters.
A simple configuration for the [domain_realm] section might look as follows:
.example.com = EXAMPLE.COM
File login.conf
The content of the file login.conf, which contains login-related settings such as the authentication method between clients and servers.
A sample configuration might look as follows:
com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required;
};
spnego-server {
com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required
refreshKrb5Config=true
storeKey=true
isInitiator=false;
};
Client module name
The name in the login.conf file for the client to be used, eg. spnego-client.
Server module name
The name in the login.conf file for the server to be used, eg. spnego-server.
LDAP user search
The following settings are required to retrieve information about the authenticated user from an Ldap (MS active directory). This data is then available in the form and can be accessed by JavaScript code.
Domain controller host
FQN (fully qualified name) and port of the active directory controller.
Example: domain.example.com Port: 389
SSL connection
When activated, all communications with the LDAP server will be encrypted with SSL.
Referral hops
The maximum number of referral hops that may be performed on the LDAP server. Setting this to 0 deactivates referral hops and no references will be followed.
User account (with domain)
This account must have been granted permission to send search queries to the active directory.
User account password
Password for the user account.
Base DN for user lookup
The LDAP baseDN used for looking up the authenticated user.
Example: ou="intern", dc="example", dc="com"
Theoretical consideration of the connection of several KDCs/domains
If multiple KDC servers or domains are desired for a global Kerberos login ability, this is theoretically possible via the standard MIT Kerberos implementation provided by Java and used by FORMCYCLE. However, the following configurations should be noted here:
- For each KDC server/domain a separate realm must be defined.
- The list to be defined under [domain_realm] must be used to specify which request URL should be handled by which realm.
- If cross realm authentication is desired, a cross realm trust must be established. This serves to the purpose that a user from realm A can also log in within the realm B. For example, this can be realized with a direct realm trust where principals are created on each relevant server against the other realms. For the realms A.REALM.COM and B.REALM.COM this would be for exemplary krbtgt/A.REALM.COM@B.REALM.COM and krbtgt/B.REALM.COM@A.REALM.COM.
- Use the same name and a strong password for the service principal or configure a keytab file.
- To query the correct user data after the Kerberos login, either an LDAP server with access to the whole forest of the realms or the functionality of the client-specific LDAP servers must be configured. It may also be necessary to adjust the responsible LDAP filter.
Make user data available to forms
The LDAP user data for the currently authenticated user are stored in the JavaScript object window.XFC_METADATA.user.rawData and can be accessed via JavaScript.
To access the property //userPrincipalName// of the user from JavaScript, use the following code:
// Auslesen der Property und Anzeige in einem Label
var elem = $('[name=txt1]');
var ldap = XFC_METADATA.user.rawData;
if(ldap.hasOwnProperty('userPrincipalName')) {
elem.html(ldap.userPrincipalName);
}
} catch (err) {}